Anatomy of a Theme
Bagisto Visual brings a modern, flexible theme system to Bagisto — heavily inspired by Shopify's proven architecture.
At its core, a theme is a structured collection of layouts, templates, sections, blocks, and settings, allowing both developers and store owners to collaboratively build and manage storefronts with ease.
By adopting a system modeled after Shopify, Bagisto Visual empowers merchants and theme developers to take full control of the storefront experience — crafting beautiful, fully customized online stores that stand out from the competition.
This section explains how a Bagisto Visual theme is organized, how the core parts fit together, and how developers and merchants can collaborate to build dynamic, customizable storefronts.
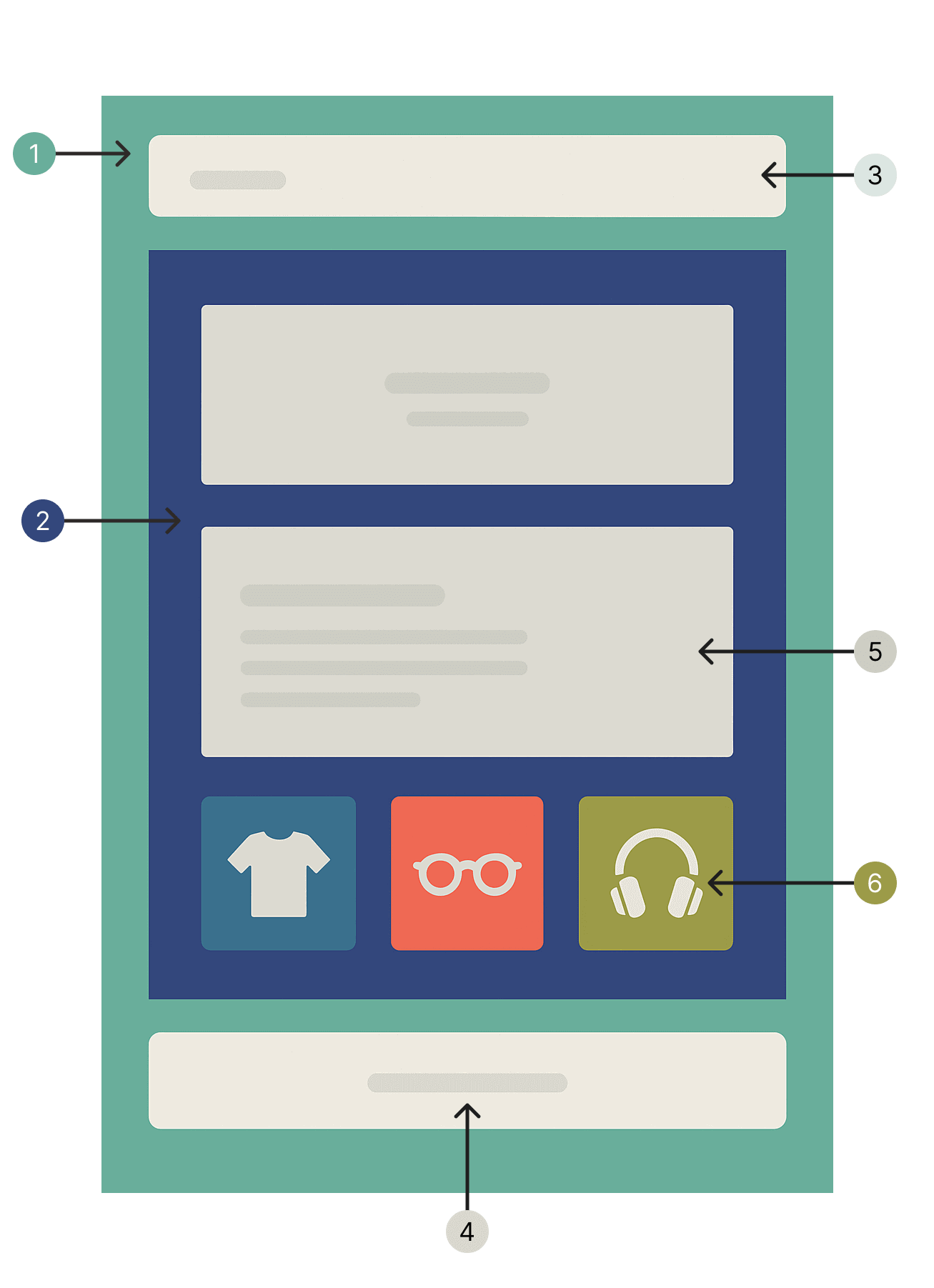
Theme Structure
A theme is made up of the following main parts:
| Number | Part | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Layout | The base structure of the page. Defines global elements and includes regions using @visualRegion(). |
| 2 | Template | Define what to render and where. Each page of the storefront has its own associated template. Templates can be Blade (with dynamic logic), JSON/YAML, or PHP. Only one template is rendered per page. |
| 3,4 | Region | Customizable zones (like header, footer) shared across all pages. Merchants can add/remove sections in regions through the Visual Editor. See Regions. |
| 5 | Template section | Modular, reusable containers that compose blocks into layouts. Used inside templates. |
| 6 | Block | Atomic, reusable components that provide content. Shared across multiple sections. The fundamental building units of v2 themes. |
Note: Templates define the structure of different page types in your storefront, such as the homepage, product pages, category pages, cart, and more. Each page is rendered based on its associated template, making it easy to create custom layouts for different parts of your store.
Folder Structure
/theme/
├── resources/
│ ├── views/
│ ├── components/ # Custom Blade or Livewire components
│ ├── layouts/ # Layouts (default layout is mandatory)
│ ├── blocks/ # Block Blade files (v2)
│ ├── sections/ # Section Blade files
│ ├── templates/ # Page templates (JSON, YAML, PHP, or Blade)
│ ├── regions/ # Region templates (header, footer, etc.)
├── src/
│ ├── Blocks/ # PHP classes for custom blocks (v2)
│ ├── Sections/ # PHP classes for custom sections
│ ├── Presets/ # Preset classes for reusable configurationsKey Concepts
Layouts
- Define the global structure of your pages.
- Must include a
default.blade.phplayout inside/resources/views/layouts/. - Layouts typically contain the
<head>, header, footer, and dynamic content area.
Templates
- Represent individual pages (e.g., homepage, product page).
- Can be written in Blade, JSON, YAML, or PHP.
- Templates list sections in the desired order.
- Only one template is rendered at a time based on the page being viewed.
Regions
- Customizable zones shared across all templates (e.g., header, footer).
- Merchants can add, remove, and reorder sections in regions through the Visual Editor.
- Created using the same formats as templates (JSON, YAML, or PHP).
- Included in layouts using the
@visualRegion()directive. - See Regions for detailed documentation.
Blocks (v2)
- Atomic, reusable components that provide content (buttons, images, headings, testimonials, product elements).
- Shared across multiple sections - define once, use everywhere.
- Created as PHP classes in
src/Blocks/with Blade views inresources/views/blocks/. - Can be nested (container blocks accept child blocks) for complex layouts.
- Two types: Dynamic (merchant-controlled) and Static (developer-controlled).
- See Core Concepts: Blocks for details.
Sections
- Containers that compose blocks into cohesive layouts.
- Accept and arrange blocks according to their schema.
- Created using PHP classes in
src/Sections/with Blade views inresources/views/sections/. - Sections provide structure; blocks provide content.